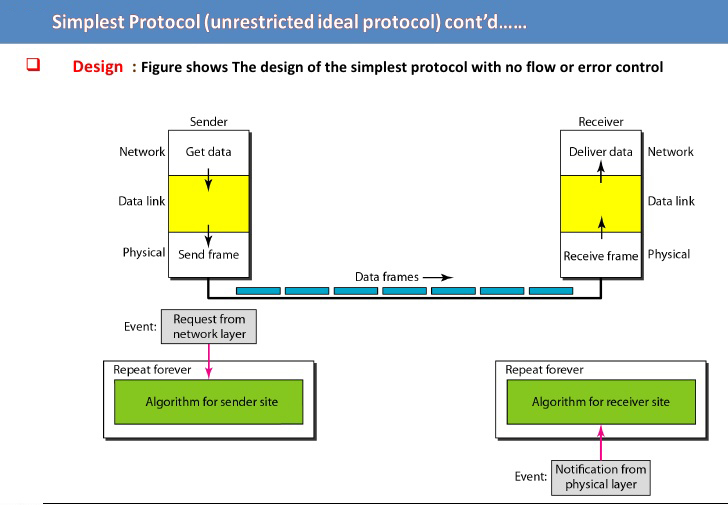
It is the simplest though unrealistic protocol with the nickname “UTOPIA“. In this case, data is transmitted in one direction only. Both the transmitting and receiving Network Layer are always ready and the proceeding time can be ignored. Infinite buffer space is available and also communication between a Data Link Layer never damages or loses frames.
Internet
Design Issues in Data Link Layer You Must Know
The design issues deal with how to make sure all frames are eventually delivered to the Network Layer at the destination and in the proper order. The usual way to ensure reliable delivery is to provide the sender with some feedback about whatever happening at the other end of the line. Typically the protocol calls for the receiver to send back special control frames bearing positive and negative acknowledgements about the incoming frames. If the sender receives a positive acknowledgement about a frame, it knows the frame has arrived safely. On the other hand, a negative acknowledgement means that something has gone wrong and the frame must be transmitted again.
Switching
A network contains a large number of computers and various intermediate devices. All these devices and computers must be joined so as to transfer data from one computer of network to any other computer. This can be possible by using two methods:-
The first method is to create an individual wire link from every computer to every other computer (like fully connected topology) this method requires a lot of wiring and will increase the system cost and efficiency. The other method is to use a technique of switching. In a switched network, special devices called switches, are used to join two or more computers and intermediate devices with each other. Switches can create temporary connection between two devices attached to the switch. These devices are hardware devices that may have a software component in them. When a particular virtual path is to be set, the switch is set accordingly, to create a path between two nodes.
A Guide to Multi-access Channels and Random Access Channels
Networks can be divided into two categories i.e., those using point-to-point connections and those using broadcast channels. Broadcast channels are sometimes referred to as multi-access channels or random access channels. The protocols used to determine who goes next on a multi-access channel belong to a sublayer of the data link layer called the MAC (Medium Access Control) sublayer. The MAC sublayer is especially important in LANs, nearly all of which use a multi-access channel to communicate. WAN, in contrast, uses point-to-point links except for satellite networks.
Framing In Computer Network Data Link Layer With Types
In order to provide services to the Network Layer, the Data Link Layer must use the service provided to it by the Physical Layer. What the Physical Layer does is, accept a raw bit stream and attempt to deliver the data to the destination. The bit stream is not guaranteed to be error-free. the number of bits received may be less than or equal to or more than the number of bits that were transmitted and they have different values. It is the task of the Data Link Layer to provide the error-free transmission of the data. The usual approach is for the Data Link Layer to break the bitstream up into discrete frames and compute the checksum for each frame. When the frame arrives at the destination the checksum is recomputed. If the newly computed checksum is different from the one contained in the frame, the Data Link Layer knows that an error has occurred and takes the necessary steps to deal with it.
What Are Common Uses of Internet
Individuals, businesses, business people, and groups largely utilize the Internet as a means of communication, with less reliance on fax machines, telephones, and the postal service. Common uses of the internet are:- Transfer of data Remote accessing E-mailing File sharing Audio, Video, and Graphics World Wide Web FTP Chat Telnet Newsgroup Transfer of data: internet … Read more
Applications of Computer Network
Computer network applications are software programs that use the Internet or other network infrastructure technology to carry out useful tasks, including file transfers inside a network. They aid in the movement of data throughout the network from one location to another.
Some of the network applications in different fields are as follows:-
- Marketing and Sales:- Computer networks are used extensively in marketing and sales organizations. Marketing professionals use them to collect, exchange and analyze data relating to customer needs and product development cycles. Sales applications include Tele-Shopping, which uses Order-Entry Computers or telephones connected to order processing networks and online reservation services for hotels, airlines, and so on.
Methods of Data Transmission
For data transmission various methods are used:-
- Synchronous Transmission
- Asynchronous Transmission
Synchronous Transmission
This method of data transmission involves block of characters that are transmitted at regular time sequences. Each of the block of characters is marked with synchronization characters. The receiving end, accepts the data block, till it detects the ending character or after a predefined number of characters are received, indicating end of a message.
Congestion in Network
Data is transferred from the source to the destination in a network. Sometimes the data is transferred in bulk in the network which affects the traffic. Now, if the traffic gets more and more in the network, therefore increasing the congestion. This leads to delay in data receiving or sending packet loss, and blocking of the connection resulting in the capacity of the network.
Network Congestion:- Network protocols are there which help in reducing the network traffic, by taking the SHORTEST PATH ALGORITHM which says that, the data is routed by seeing the shortest path of the desired destination.
Network Topologies
Topologies:-is the arrangement of the nodes in a network.There are basic topologies used:
- Mesh
- Star
- Ring
- Tree
- Bus
- Hybrid